Definition and purpose of OTC hearing aids in the USA Design and main components of hearing aid devices Intended users and usage conditions for OTC products FDA regulatory framework for OTC hearing aids Compliance with safety and product standards
Hearing aids for seniors in the USA are devices developed to support communication by amplifying sound in daily environments. These aids often include features such as adjustable volume, directional microphones, and compatibility with mobile applications. Their use requires proper fitting and guidance from licensed professionals, ensuring compliance with medical device regulations and safety standards.
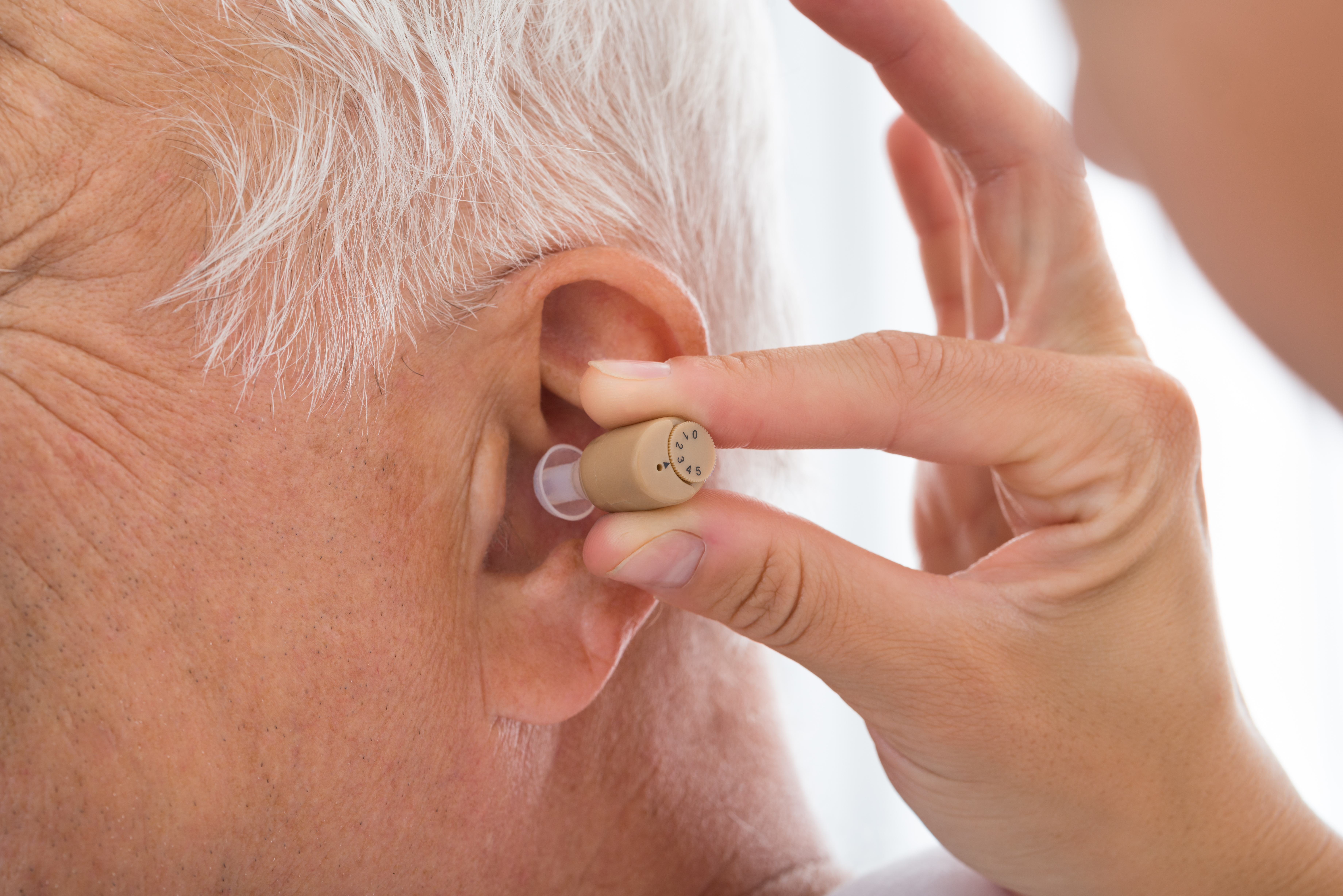
Design and Main Functions of Hearing Aids for Seniors
OTC hearing aids share many design elements with traditional prescription hearing aids but are specifically configured for straightforward user setup and adjustment. Most devices consist of a microphone to capture sound, an amplifier to increase sound volumes, a speaker (receiver) that delivers the enhanced sound into the ear, and a battery for power. Their primary function is to selectively amplify sounds in frequency ranges where users experience hearing loss while minimizing background noise.
For seniors specifically, many OTC devices feature larger controls to accommodate dexterity challenges and simplified interfaces requiring minimal technical knowledge. Some incorporate tinnitus masking features, as tinnitus commonly accompanies age-related hearing loss. Modern OTC devices also typically offer multiple listening profiles that can be selected based on different environments, from quiet home settings to noisier public spaces like restaurants or social gatherings.
Adjustable Volume and Directional Microphone Features
A key advantage of OTC hearing aids is their user-adjustable settings that allow wearers to modify sound reception based on their environment and preferences. Most devices include volume controls that can be adjusted throughout the day as listening needs change. These controls range from simple dial adjustments to digital button interfaces, depending on the technology level of the device.
Directional microphone technology represents one of the most valuable features in modern OTC hearing aids. Unlike omnidirectional microphones that capture sounds equally from all directions, directional microphones prioritize sounds coming from in front of the wearer while reducing sounds from the sides and rear. This technology significantly improves speech understanding in noisy environments, where traditional hearing aids might amplify all sounds indiscriminately. Advanced OTC models often include adaptive directional microphone systems that automatically adjust based on the acoustic environment, switching between omnidirectional mode in quiet settings and directional mode in noisier situations.
Compatibility with Mobile Applications in Modern Devices
The integration of wireless technology has revolutionized how users interact with their hearing aids. Many contemporary OTC devices feature Bluetooth connectivity that enables direct pairing with smartphones, tablets, and other compatible devices. This wireless capability allows for direct audio streaming of phone calls, music, and other media directly to the hearing aids.
Companion mobile applications extend the functionality of OTC hearing aids significantly, offering features like:
-
Remote adjustment of volume and sound profiles without touching the device
-
Customization of frequency response based on specific hearing needs
-
Creation and storage of multiple listening programs for different environments
-
Battery monitoring and maintenance reminders
-
Sound therapy options for tinnitus management
-
Location-based automatic setting adjustments that remember preferred settings for frequently visited places
These applications transform smartphones into hearing aid control centers, allowing discreet adjustments without drawing attention to the device itself—an important consideration for many users concerned about stigma associated with hearing aid use.
Professional Fitting Procedures for Safe Usage
While OTC hearing aids are designed for self-fitting, professional guidance remains valuable for optimal outcomes. The initial self-fitting process typically involves a smartphone-based hearing test that helps establish baseline sound amplification settings. Users then make adjustments based on their perception and comfort with amplified sound in various environments.
For safety and effectiveness, many hearing health experts recommend an initial consultation with an audiologist before purchasing an OTC device. This professional can:
-
Conduct a comprehensive hearing evaluation to confirm suitability for OTC devices
-
Rule out medical conditions requiring treatment rather than amplification
-
Provide guidance on selecting appropriate OTC devices based on specific hearing loss patterns
-
Offer instructions on proper insertion and care to prevent ear canal irritation or damage
-
Suggest complementary communication strategies to enhance hearing aid benefits
Some OTC hearing aid manufacturers offer remote fitting assistance or provide access to hearing professionals who can help optimize device settings through telehealth appointments, bridging the gap between traditional prescription models and the self-service OTC approach.
Compliance with U.S. Medical Device Regulations
OTC hearing aids must meet strict regulatory requirements established by the FDA’s final rule issued in August 2022. These regulations ensure devices meet performance standards while remaining accessible to consumers without professional intervention. Key regulatory elements include:
The FDA categorizes OTC hearing aids as Class I or Class II medical devices, with specific performance requirements including:
-
Maximum output limits to prevent further hearing damage
-
Consistent gain across specified frequency ranges
-
Distortion control standards
-
Self-generated noise limitations
-
Processing delay restrictions
Manufacturers must register their facilities with the FDA and list their OTC hearing aid products, following quality system regulations that govern design, manufacturing, packaging, and labeling. Labeling requirements are particularly stringent, mandating clear instructions for use, warnings about when to consult a physician, information about warranty terms, and a statement that the device is intended for adults with perceived mild to moderate hearing loss.
The FDA also requires manufacturers to maintain complaint files and report serious adverse events, ensuring ongoing safety monitoring of devices in the market. These regulations aim to balance innovation and accessibility with consumer protection in a category where improper amplification could potentially cause harm.
OTC hearing aids represent a significant advancement in hearing healthcare accessibility, offering affordable options for millions of Americans experiencing mild to moderate hearing loss. By understanding their design, features, fitting procedures, and regulatory framework, consumers can make informed decisions about whether these devices might be appropriate for their hearing needs.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.




