Exploring Cleaning and Sanitation Procedures: Roles and Responsibilities
Cleaning and sanitation procedures are central to maintaining health standards in workplaces, restaurants, and public facilities. This article examines the roles involved in sanitation work, the responsibilities tied to hygiene, and the practices that ensure consistent results.
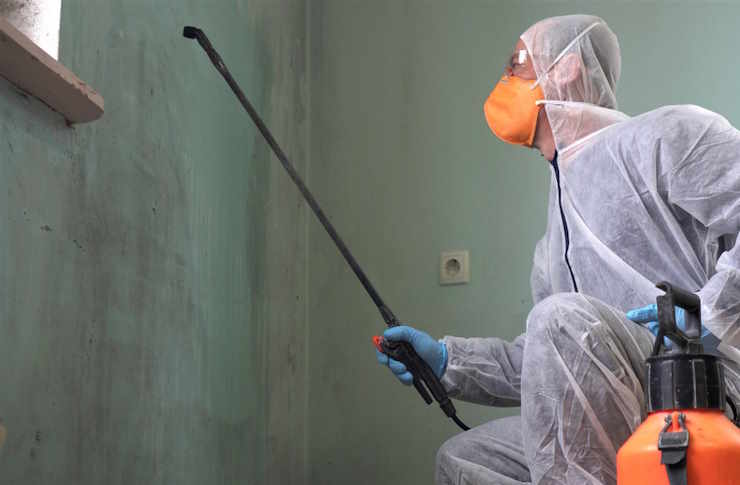

The cleaning and sanitation industry represents a vital sector of the modern economy, encompassing roles that ensure public health and safety across countless facilities. From healthcare environments to educational institutions, professional cleaning personnel serve as the frontline defenders against contamination and disease transmission. These positions demand a comprehensive understanding of hygiene principles, regulatory compliance, and specialized cleaning methodologies.
What Responsibilities Are Involved in Cleaning and Sanitation Procedures?
Cleaning professionals handle numerous critical tasks that maintain facility safety and cleanliness. Daily responsibilities typically include surface disinfection, waste management, and equipment maintenance. Personnel must follow established protocols for different environments, ensuring appropriate chemical usage and application techniques. Documentation of cleaning activities, inventory management of supplies, and adherence to safety procedures form additional core responsibilities. Emergency response cleaning, such as spill containment or biohazard cleanup, may also fall within their scope of duties.
What Skills Support Effective Hygiene Management?
Successful hygiene management requires both technical knowledge and practical abilities. Understanding chemical properties, dilution ratios, and compatibility between different cleaning agents prevents dangerous reactions and ensures effectiveness. Time management skills enable efficient completion of tasks within designated schedules. Physical stamina and attention to detail support thorough cleaning execution. Communication abilities facilitate coordination with team members and reporting of maintenance issues or safety concerns. Problem-solving skills help address unexpected situations and adapt procedures to unique circumstances.
What Practices Ensure Compliance with Sanitation Standards?
Compliance with sanitation standards involves systematic implementation of established protocols and regular monitoring procedures. Personnel must maintain current knowledge of relevant regulations, including OSHA guidelines, EPA requirements, and industry-specific standards. Regular training updates ensure awareness of new procedures and regulatory changes. Documentation practices, including cleaning logs and inspection records, provide accountability and traceability. Quality control measures, such as ATP testing or visual inspections, verify cleaning effectiveness. Proper personal protective equipment usage and chemical storage procedures prevent violations and ensure worker safety.
| Service Type | Provider | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Commercial Cleaning | ServiceMaster | Multi-industry expertise, quality assurance programs |
| Healthcare Sanitation | Crothall Healthcare | Specialized infection control protocols |
| Educational Facilities | ABM Industries | Student-safe cleaning products, flexible scheduling |
| Industrial Cleaning | UNICCO Service | Heavy-duty equipment, hazardous material handling |
| Hospitality Services | Aramark | Guest satisfaction focus, rapid response capabilities |
The cleaning and sanitation field continues evolving with technological advances and changing health requirements. Green cleaning initiatives promote environmentally sustainable practices while maintaining effectiveness standards. Automated cleaning systems and smart monitoring technologies enhance efficiency and consistency. Professional development opportunities within the industry include specialized certifications, supervisory roles, and facility management positions.
Career advancement in cleaning and sanitation often involves developing expertise in specific sectors or obtaining industry certifications. Leadership roles may include training new personnel, managing supply inventories, or overseeing quality assurance programs. The growing emphasis on infection control and environmental health creates expanding opportunities for skilled professionals who understand complex sanitation requirements and can implement comprehensive hygiene management systems.