Welding Careers – Equipment and Industry Standards
Welding careers rely on advanced equipment, structured franchise training, and digital software support. Professionals in this field use protective tools, cutting machines, and monitoring systems to ensure safety, efficiency, and long-term career development in the welding industry.
How Equipment Defines Quality and Safety in Welding Careers
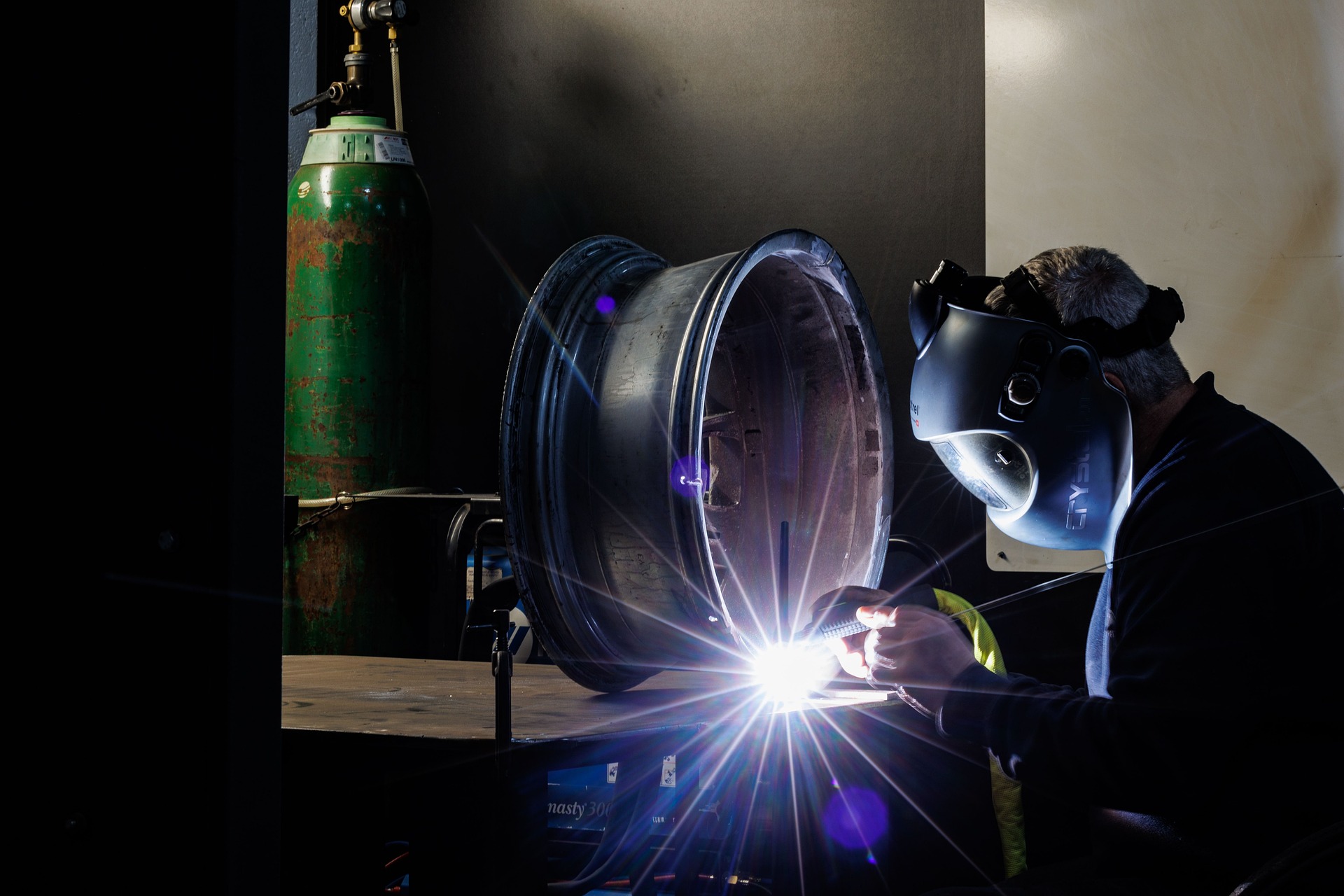
Modern welding equipment directly impacts both work quality and workplace safety standards. Professional-grade welding machines provide consistent arc stability, precise temperature control, and reliable power output essential for creating strong, durable joints. Safety equipment including welding helmets with auto-darkening filters, fire-resistant clothing, and proper ventilation systems protect welders from hazardous fumes, intense light, and extreme temperatures.
Quality welding equipment reduces defects, minimizes rework, and ensures compliance with industry codes such as AWS D1.1 for structural welding. Employers typically invest in reliable brands like Lincoln Electric, Miller Electric, and ESAB to maintain production standards and worker safety protocols.
Do Franchise Systems Provide Structured Training and Growth
Welding franchise operations offer systematic training programs that combine classroom instruction with hands-on experience. These structured environments provide apprenticeships, certification preparation, and career advancement pathways within established business frameworks. Franchise systems often maintain relationships with local technical schools and industry organizations to ensure training meets current market demands.
Many welding franchises focus on specialized services such as mobile welding, fabrication, or repair services. This approach allows new welders to gain experience in specific niches while building business skills and customer relationships under proven operational models.
How Software Platforms Monitor Tasks and Improve Efficiency
Digital management systems increasingly support welding operations through project tracking, quality documentation, and workflow optimization. Software platforms help monitor welding parameters, track consumable usage, and maintain certification records for compliance purposes. These systems improve efficiency by scheduling jobs, managing inventory, and generating reports for quality assurance.
Advanced welding equipment now integrates with digital platforms to record welding data, enabling supervisors to analyze performance trends and identify areas for improvement. This technology supports continuous professional development and helps welders refine their techniques based on objective performance metrics.
Industry Standards and Certification Requirements
Welding careers require adherence to established codes and standards developed by organizations like the American Welding Society (AWS), American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME), and American Petroleum Institute (API). These standards define acceptable welding procedures, material specifications, and testing requirements for different applications.
Professional welders typically pursue certifications specific to their chosen specialties. Structural welding certifications differ from pipeline welding credentials, and aerospace welding requires additional specialized training. Maintaining current certifications involves periodic testing and continuing education to stay current with evolving industry practices.
Career Paths and Specialization Options
Welding careers extend beyond basic fabrication work to include specialized positions such as welding inspectors, underwater welders, and robotic welding technicians. Experienced welders often advance to supervisory roles, become welding engineers, or start their own fabrication businesses. The aerospace and energy sectors offer premium positions requiring advanced certifications and extensive experience.
Geographic location significantly influences career opportunities and salary potential. Industrial regions with manufacturing, shipbuilding, or energy production typically offer more positions and competitive compensation packages for skilled welders.
| Career Level | Average Annual Salary | Required Experience | Typical Certifications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Entry-Level Welder | $35,000 - $45,000 | 0-2 years | Basic AWS certification |
| Experienced Welder | $45,000 - $65,000 | 2-5 years | Multiple process certifications |
| Specialized Welder | $55,000 - $85,000 | 5+ years | Advanced certifications (6G, API) |
| Welding Inspector | $60,000 - $90,000 | 5+ years | CWI certification |
| Welding Supervisor | $70,000 - $100,000 | 8+ years | Management + technical certifications |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
The welding industry continues evolving with technological advances including automated systems, improved materials, and enhanced safety equipment. Career success depends on continuous learning, maintaining current certifications, and adapting to new welding technologies and industry requirements. Professional welders who invest in quality equipment, pursue ongoing training, and develop specialized skills typically enjoy stable employment and advancement opportunities throughout their careers.