Welding Careers in Japan – Skills and Work Environments
Welding jobs in Japan involve joining and repairing metal structures in industries such as construction, shipbuilding, and manufacturing. This article highlights common tasks, essential skills, and safety measures that define welding careers in different work environments.
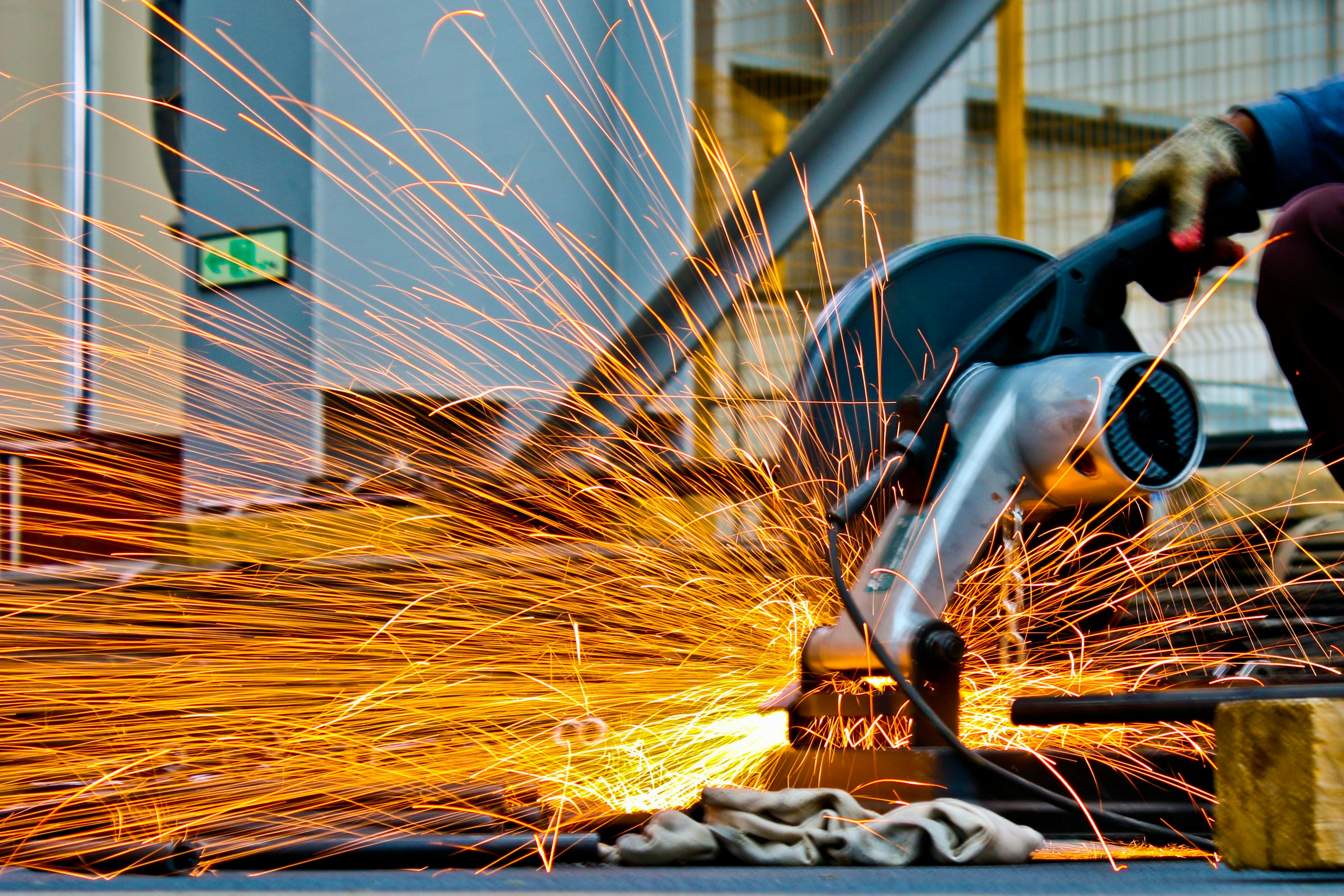

What are the core welding methods and applications in Japan?
Japanese welders utilize a range of welding techniques to meet the diverse needs of industries across the country. The most common welding methods employed in Japan include:
-
Arc Welding: This versatile method is widely used in construction and heavy machinery manufacturing. It involves creating an electric arc between an electrode and the base material to melt and join metals.
-
TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) Welding: Prized for its precision, TIG welding is often used in the automotive and aerospace industries. It produces clean, high-quality welds on thin materials and is particularly useful for joining non-ferrous metals.
-
MIG (Metal Inert Gas) Welding: Also known as GMAW (Gas Metal Arc Welding), this method is popular in automotive manufacturing and general fabrication due to its speed and efficiency.
-
Resistance Welding: Commonly used in the electronics and automotive industries, this technique joins metals by applying pressure and passing an electric current through the materials.
-
Laser Welding: Gaining popularity in Japan’s high-tech industries, laser welding offers precise, high-speed joining of metals with minimal heat-affected zones.
These welding methods find applications across various sectors, from shipbuilding and automotive manufacturing to electronics and construction.
Which industries commonly employ welders in Japan?
Welders in Japan find employment opportunities across a diverse range of industries, reflecting the country’s robust manufacturing and construction sectors. Some of the key industries employing welders include:
-
Automotive Manufacturing: Japan’s renowned automotive industry relies heavily on skilled welders for vehicle body assembly, chassis fabrication, and component production.
-
Shipbuilding: With its extensive coastline, Japan has a significant shipbuilding industry that requires welders for constructing and repairing vessels of all sizes.
-
Construction: Welders play a crucial role in Japan’s construction sector, working on skyscrapers, bridges, and other infrastructure projects.
-
Aerospace: The country’s growing aerospace industry employs welders for manufacturing aircraft components and spacecraft structures.
-
Electronics: Precision welding is essential in Japan’s electronics industry for producing circuit boards and other delicate components.
-
Energy Sector: Welders are needed for building and maintaining power plants, including nuclear facilities and renewable energy installations.
-
Railway Industry: Japan’s extensive rail network requires welders for track maintenance, train manufacturing, and infrastructure development.
These industries offer a variety of work environments, from large manufacturing plants to outdoor construction sites, providing welders with diverse career options.
What safety practices are essential in Japanese welding environments?
Safety is paramount in Japanese welding environments, with strict regulations and practices in place to protect workers. Key safety measures include:
-
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Welders must wear appropriate PPE, including welding helmets with auto-darkening filters, flame-resistant clothing, safety glasses, and steel-toed boots.
-
Ventilation Systems: Proper ventilation is crucial to remove harmful fumes and gases produced during welding processes, especially in enclosed spaces.
-
Fire Prevention: Welding areas are equipped with fire extinguishers and fire-resistant materials to prevent and control potential fires.
-
Electrical Safety: Regular inspection and maintenance of welding equipment ensure electrical safety and prevent accidents.
-
Training and Certification: Japanese welders undergo rigorous training and certification processes to ensure they understand and follow safety protocols.
-
Ergonomic Considerations: Workstations are designed to minimize physical strain and repetitive stress injuries common in welding professions.
-
Radiation Protection: For processes like X-ray inspection of welds, proper shielding and monitoring are implemented to protect workers from radiation exposure.
-
Regular Health Check-ups: Welders in Japan typically undergo periodic health examinations to monitor for potential occupational health issues.
These safety practices are strictly enforced and regularly updated to maintain high standards of occupational safety in Japan’s welding industry.
What skills and qualifications are required for welding careers in Japan?
Aspiring welders in Japan need to develop a specific set of skills and obtain relevant qualifications to succeed in their careers:
-
Technical Skills: Proficiency in various welding techniques, ability to read and interpret technical drawings, and knowledge of metallurgy are essential.
-
Certification: The Japan Welding Engineering Society (JWES) offers certifications that are widely recognized in the industry. These include qualifications for different welding methods and materials.
-
Language Skills: While not always mandatory, knowledge of Japanese can be beneficial, especially for understanding safety instructions and communicating with colleagues.
-
Attention to Detail: Japanese industries are known for their high-quality standards, making precision and attention to detail crucial skills for welders.
-
Physical Fitness: Welding often involves working in challenging positions and environments, requiring good physical condition and stamina.
-
Adaptability: The ability to work with new technologies and adapt to changing industry standards is important in Japan’s evolving manufacturing landscape.
-
Safety Consciousness: A strong understanding of safety protocols and the ability to maintain a safe working environment is essential.
Welders who possess these skills and qualifications are well-positioned for successful careers in Japan’s diverse industrial sectors.
In conclusion, welding careers in Japan offer diverse opportunities across various industries, requiring a blend of technical skills, safety awareness, and adaptability. The country’s commitment to quality and innovation in manufacturing ensures that skilled welders remain in demand, contributing significantly to Japan’s industrial success.